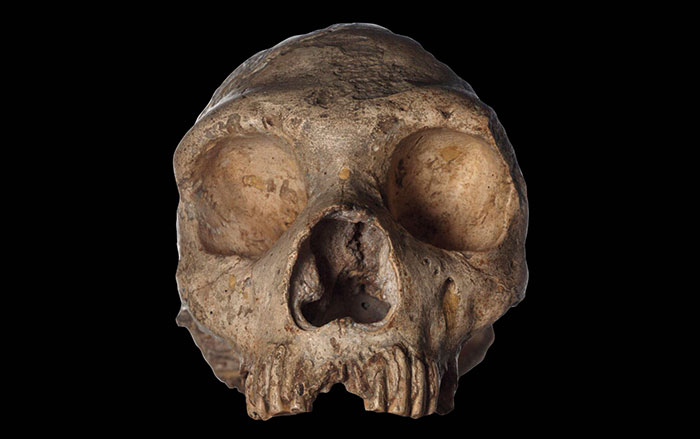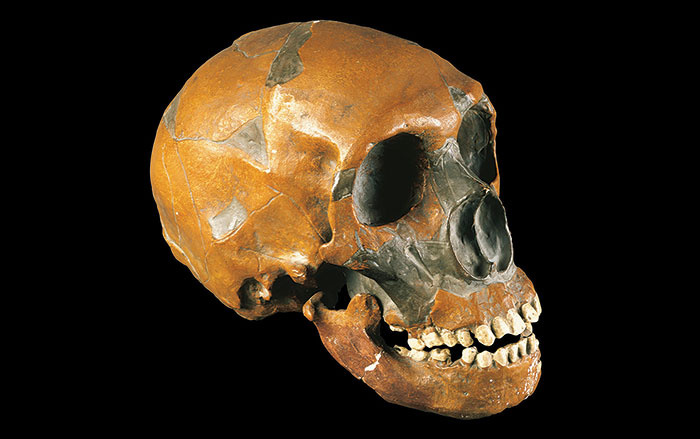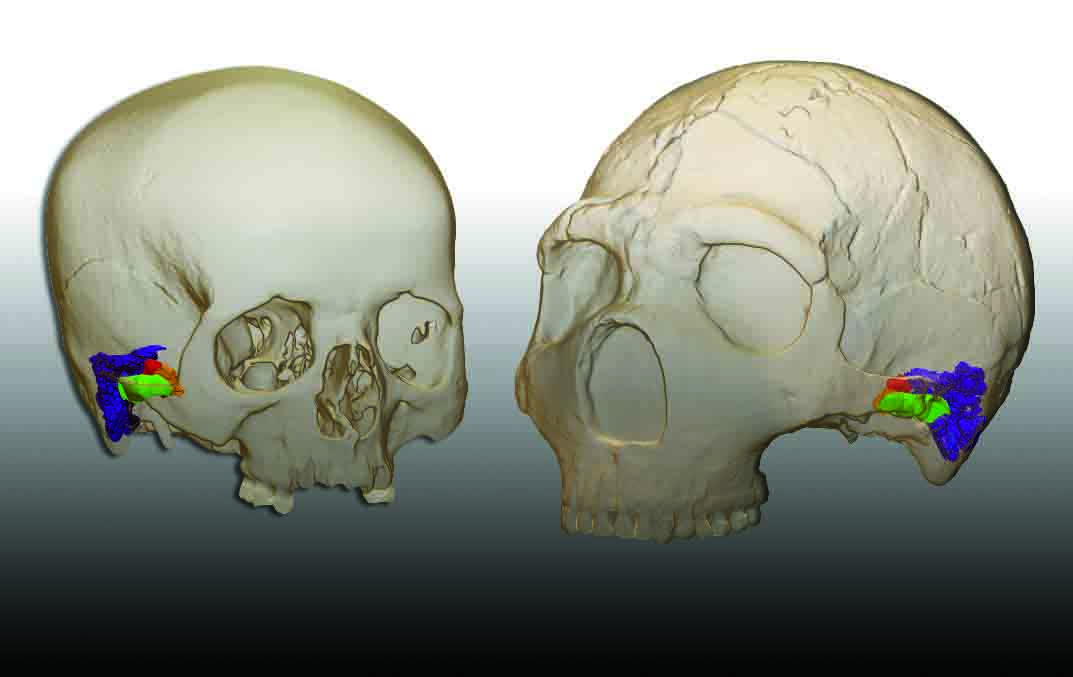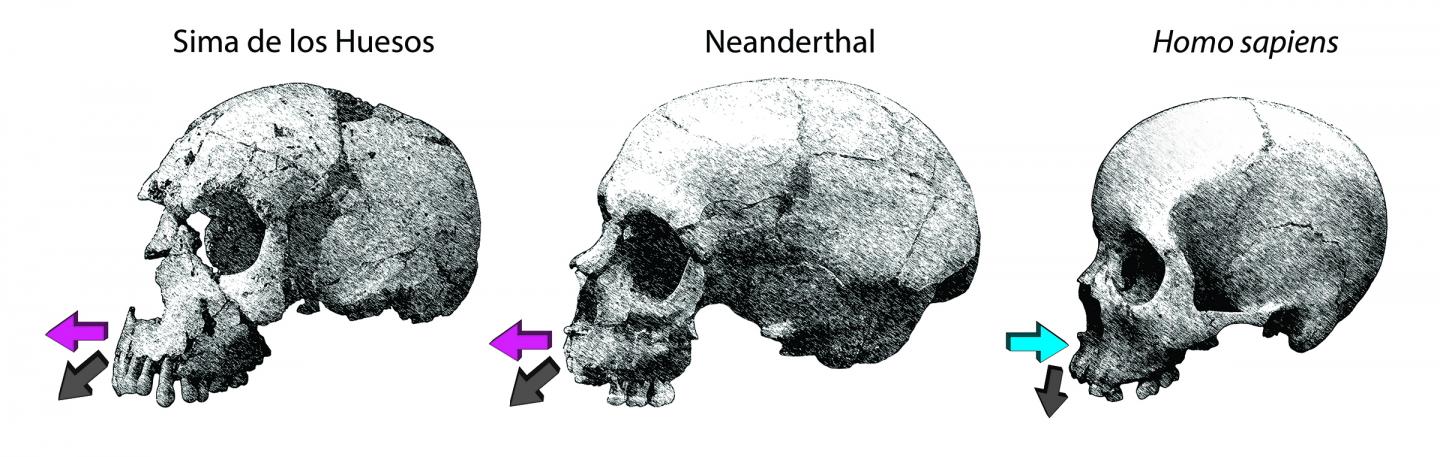
NEW YORK, NEW YORK—A study of facial growth patterns, led by Rodrigo Lacruz of New York University has, has found a developmental difference between Neanderthals and modern humans. The international team of scientists used an electron microscope and a portable confocal microscope to examine the outer layer of facial skeletons of young Neanderthals from Gibraltar and from the La Quina site in southwestern France. These results were compared with the 400,000-year-old faces of hominin teenagers discovered in the Sima do los Huesos in north-central Spain, who are thought to be likely Neanderthal ancestors. The study found that in modern human children, the outermost layer of bone in the face has many osteoclast cells, which break down bone. The faces of young Neanderthals have many osteoblasts, or bone forming cells. “We always considered Neanderthals to be a very different category of hominin. But in fact they share with older African hominins a similar facial growth pattern. It’s actually humans … that deviated from the ancestral pattern,” Lacruz explained in a press release. For more, go to "Your Face: Punching Bag or Spandrel?"